The words, the pauses, the syllables, the phones, and even some subphonemic events are located in the recorded signal.
单词、短语、 节、
节、 素,甚
素,甚
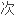

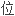
 件等元素都由录
件等元素都由录 信号记录下来。
信号记录下来。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
 词汇
词汇 (4) Assimilation: It refers to the change of a sound by the influence of an adjacent sound, which is more specifically called " contact" or " contiguous" assimilation.
(1) 脱落:语 脱落是指
脱落是指 位系统中作为
位系统中作为 位
位 某个语
某个语
 消失。语
消失。语 脱落也可以在语句中发生,往往是某些非重读元
脱落也可以在语句中发生,往往是某些非重读元 发生脱落。(2) 添加:添加是指把某些语
发生脱落。(2) 添加:添加是指把某些语 添加到语
添加到语 原有
原有 链条上。(3) 换位:换位是指语流中一种可供选择
链条上。(3) 换位:换位是指语流中一种可供选择 方法。(4) 同化:同化是指由于邻近语
方法。(4) 同化:同化是指由于邻近语
 影响而产生
影响而产生 语
语 变化,更明确
变化,更明确 叫法是" 接触" 同化或" 邻近" 同化。
叫法是" 接触" 同化或" 邻近" 同化。
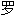
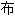
 词汇
词汇 (4) Narrow Transcriptional called phonetic transcription, which shows more phonetic details, either just by using more specific symbols or by also representing some allophonic differences. The use of diacritics is a means of increasing precision.
(4) 狭义转录称为语 转录,它通过使用更具体
转录,它通过使用更具体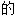 符号或还表示一些
符号或还表示一些 位差异来显示更多
位差异来显示更多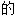 语
语 细节。使用变
细节。使用变 符号是提高精度
符号是提高精度 一种手段。
一种手段。
Ever since its publication in the middle of the 1960s, this research paradigm has become the mainstream in sociolinguistics and been alternatively termed as " the quantitative paradigm, sociolinguistics proper, variationist studies, urban dialectology and secular linguistics." (Fasold, 1999 [1990])
20 世纪 60 年代中期,著名社会语言学家威廉・拉波夫(William Labov)在纽约市 几个部门进行了一次彻底
几个部门进行了一次彻底 调查。这项调查
调查。这项调查 目
目 是研究
是研究 话者
话者
 位变化如何代表他们
位变化如何代表他们 社会地位。这项调查
社会地位。这项调查 结果发表在《纽约市英语
结果发表在《纽约市英语 社会分层》(1966)中,该书现已成为社会语言学
社会分层》(1966)中,该书现已成为社会语言学 经典著作。结果表明,阶级和文体是影响
经典著作。结果表明,阶级和文体是影响 话者选择一种
话者选择一种 位变体而不是另一种
位变体而不是另一种 位变体
位变体 两个主要因素。基于这些发现,拉波夫明确阐述了阶级和文体分层
两个主要因素。基于这些发现,拉波夫明确阐述了阶级和文体分层 模式。他
模式。他 工作更重要
工作更重要 是,它成功地将阶级引入社会语言学研究中作为一个不可或缺
是,它成功地将阶级引入社会语言学研究中作为一个不可或缺 变量。自 20 世纪 60 年代中期出版以来,这种研究范式已成为社会语言学
变量。自 20 世纪 60 年代中期出版以来,这种研究范式已成为社会语言学 主流,并被交替称为 “定量范式、适当
主流,并被交替称为 “定量范式、适当 社会语言学、变异研究、城市方言学和世俗语言学”(Fasold,1999 [1990])。
社会语言学、变异研究、城市方言学和世俗语言学”(Fasold,1999 [1990])。