Prolonged droughts have also led to desertification.
长期的干旱会导致沙漠化。
The raising of livestock is a major economic activity in semiarid lands, where grasses are generally the dominant type of natural vegetation.
导致沙漠化的主要因素有四个:过度种植,过度放牧,过分砍伐,过度灌溉。由于人口密度增加,人们对粮食作物的种植已经扩展到日益干燥的区域进行。这些区域很有可能经常会发生干旱,所以农作物种植失败是很正常的事情。大多数农作物的种植需要事先移除天然植被,而农作物欠收后又会留下大面积
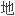 ,非常容易被风力和雨水侵蚀。草类通常是当
,非常容易被风力和雨水侵蚀。草类通常是当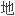 的主要天然植被类型。
的主要天然植被类型。
Even in the areas that retain a soil cover, the reduction of vegetation typically results in the loss of the soil's ability to absorb substantial quantities of water.
沙漠化主要通过以下过程实现:首先自然植被不断减少,随后风力和雨水加速了土壤的腐蚀。有的时候松散的土壤全部被风刮走,留下石质化的表层;其它情况下细小的沙粒可能会被吹走,而正常沙粒大小的砂子不断堆积,从而形成移动的沙丘或者沙脊。植被的减少通常也会导致土壤吸收大量水的能力丧失。
The extreme seriousness of desertification results from the vast areas of land and the tremendous numbers of people affected, as well as from the great difficulty of reversing or even slowing the process.
造成土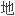 沙漠化的最后一个主要人为因素在于人类过度灌溉导致土壤的盐碱化。灌溉多余的水渗透到
沙漠化的最后一个主要人为因素在于人类过度灌溉导致土壤的盐碱化。灌溉多余的水渗透到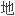 下水位。假如没有排水系统的存在,那么
下水位。假如没有排水系统的存在,那么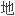 下水位上
下水位上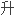 ,把溶解的盐分带到土壤表面。水分蒸发后,盐分留在了表面,形成白色的
,把溶解的盐分带到土壤表面。水分蒸发后,盐分留在了表面,形成白色的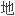 壳层,这一
壳层,这一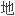 壳层阻止了空气和水接触
壳层阻止了空气和水接触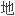 底下的土壤。以及扭转甚至减缓这一过程的巨大困难。
底下的土壤。以及扭转甚至减缓这一过程的巨大困难。